With high speed 3D printing becoming more prominent due to the introduction of high speed 3D printers, We are excited to introduce a range of new and existing upgraded materials to our assortment. These materials, while still suitable for traditional printers, have also been fully optimized for the new high speed 3D printing technology. Do keep in mind that faster print speeds also require higher print temperatures.
High Precision PLA
High Precision PLA is a more dense and resilient PLA filament that is developed for consistent batch-to-batch production. The filament has guaranteed precision on diameter, ovality, shrinkage, and color tolerances. The diameter and ovalness of High Precision PLA filament are measured via a continuous 3-axis laser measurement. A 3-axes measurement is far more accurate and ensures that there are no blind spots around the diameter. High Precision PLA filaments are RAL-color matched.
3-axis laser measurement
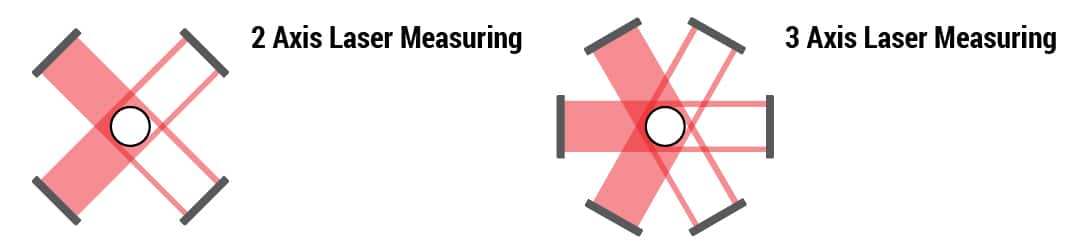
By using laser measuring from 3 different angles we are able to not only produce a highly accurate 1.75mm diameter filament, but also ensure the roundness of the filament. During this process, the filament is continuously measured and any deviations from the desired diameter are automatically corrected.
We are using a laser micrometer, this type of sensor uses a laser beam to measure the diameter of a material as it passes through the sensor. The laser micrometer sends the measurement data to a control system, which compares the measured diameter to the desired diameter. If a deviation is detected, the control system sends a signal to the equipment. This process can improve the quality and consistency of the material being produced, by reducing variations in diameter and ensuring that the material meets the desired specifications. The device measures on 3 axis as shown on the image above. This has a reduced blind spot compared to 1 or 2 axis measurement which are more standard in the industry.
Precise RAL color matching
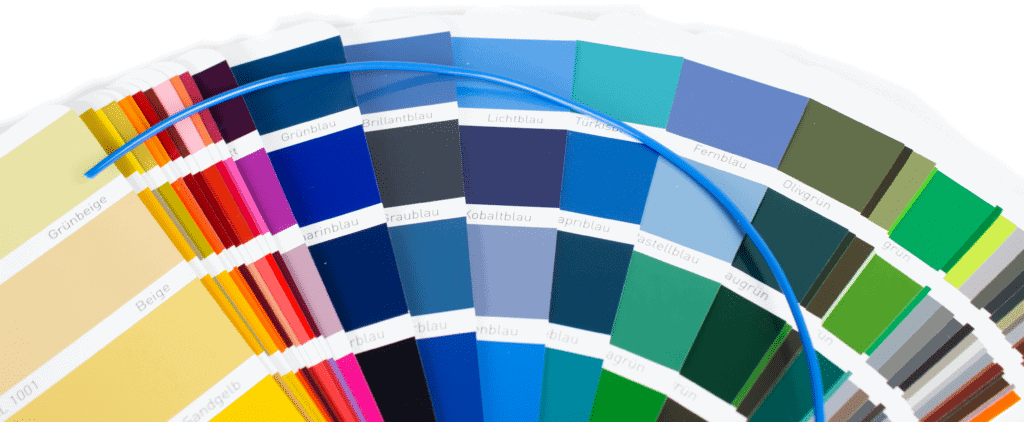

RAL is a color matching system used to define standard colors for paint, coatings, and plastics. The system was developed by the German RAL organization (Reichsausschuss für Lieferbedingungen und Gütesicherung) in 1927 and is now used worldwide. The RAL color system includes more than 2,000 standardized colors, each identified by a unique four-digit code. The colors are divided into six color families: RAL Classic, RAL Design, RAL Effect, RAL Plastics, RAL Digital, and RAL Next. The RAL color system uses a variety of methods to measure and specify colors, including visual color matching, spectrophotometry, and colorimetry.
Visual color matching is the most common method used in the RAL color system. This method involves comparing a sample of the color to be matched with a set of standard RAL color swatches under controlled lighting conditions. The color swatch that most closely matches the sample is then assigned the corresponding RAL color code. Using a more precise method of measuring color that involves analyzing the color of a sample using a spectrophotometer. This instrument measures the amount of light reflected or transmitted by a sample at different wavelengths, and generates a spectral curve that can be compared to the standard RAL spectral curves to determine the closest match.